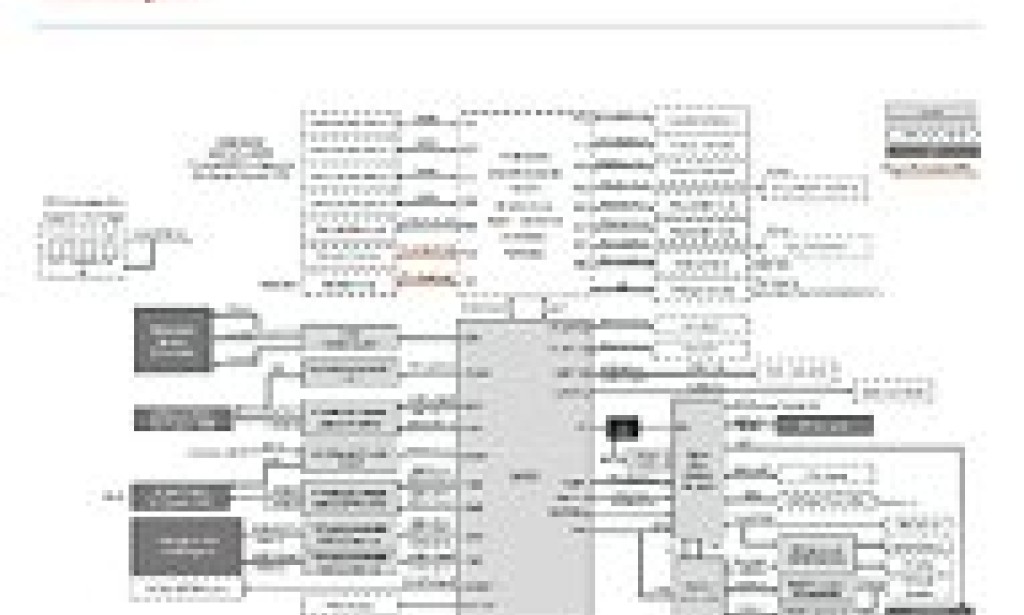
The platform introduces a new Socket E2 design with 4,710 LGA pins built to support CPUs with TDP ratings reaching 350 watts. Intel is taking a two-tier approach with distinct "Expert" and "Mainstream" configurations: Expert-class implementations unlock 112 PCIe lanes (96 PCIe 5.0 lanes plus 16 PCIe 4.0 lanes), while the Mainstream tier delivers 80 PCIe 5.0 lanes. This will support a XCC-based "Granite Rapids-WS" processor with 86 cores and 172 threads, achieving single-core boost speeds near 4.8 GHz with 336 MB of L3 cache.
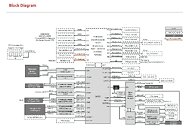
Memory capabilities mark a significant evolution from previous workstation platforms. The W890 chipset supports both standard DDR5 DIMMs and registered DDR5 modules, with RDIMMs validated for speeds up to 5,200 MT/s. In a quad-channel configuration with two DIMMs per channel, systems can address up to 2 TB of memory per processor socket. The connectivity suite includes a 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet controller, numerous USB 3.2 and USB 2.0 ports, multiple SATA III interfaces, and dual SlimSAS connectors that each provide PCIe 4.0 x4 bandwidth. Server-grade management infrastructure includes an ASPEED AST2600 BMC and a Nuvoton system supervisor, while power delivery provisions mandate a standard 24-pin ATX connector alongside support for up to four supplementary 8-pin CPU power headers.The W890 positions Intel to compete directly with AMD's Threadripper ecosystem in the premium HEDT segment. Although AMD continues to lead in maximum core counts and cache capacity, Intel's refined platform counters with improved memory speeds and a flexible PCIe topology designed to optimize throughput. The W890 represents a significant advancement over the current W790 generation, particularly in memory subsystem performance. All eyes are on CES 2026 when Intel is expected to officially unveil the platform. However, final evaluations will depend on the production processor specifications and motherboard designs.


You must be logged in to post a comment.