Applications and devices equipped with AI can see and identify objects. They can understand and respond to human language. They can learn from new information and experience. They can make detailed recommendations to users and experts. They can act independently, replacing the need for human intelligence or intervention (a classic example being a self-driving car).
But in 2024, most AI researchers, practitioners and most AI-related headlines are focused on breakthroughs in generative AI (gen AI), a technology that can create original text, images, video and other content. To fully understand generative AI, it’s important to first understand the technologies on which generative AI tools are built: machine learning (ML) and deep learning.
Think Newsletter
Join over 100,000 subscribers who read the latest news in tech
Stay up to date on the most important—and intriguing—industry trends on AI, automation, data and beyond with the Think newsletter. See the IBM Privacy Statement.
Machine learning
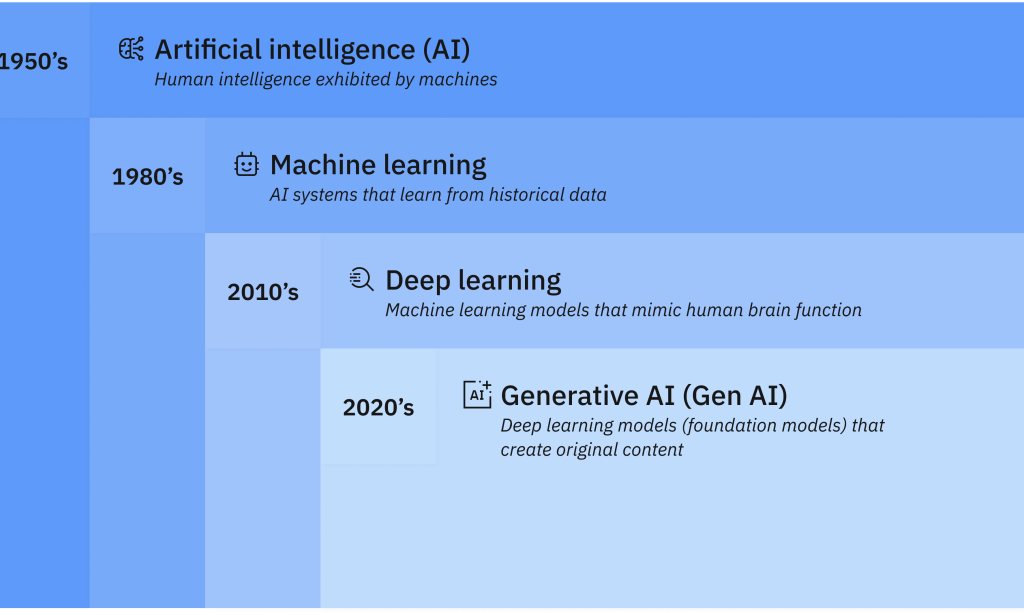
A simple way to think about AI is as a series of nested or derivative concepts that have emerged over more than 70 years:

How artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning and generative AI are related.
Directly underneath AI, we have machine learning, which involves creating models by training an algorithm to make predictions or decisions based on data. It encompasses a broad range of techniques that enable computers to learn from and make inferences based on data without being explicitly programmed for specific tasks.
There are many types of machine learning techniques or algorithms, including linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, random forest, support vector machines (SVMs), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), clustering and more. Each of these approaches is suited to different kinds of problems and data.
But one of the most popular types of machine learning algorithm is called a neural network (or artificial neural network). Neural networks are modeled after the human brain's structure and function. A neural network consists of interconnected layers of nodes (analogous to neurons) that work together to process and analyze complex data. Neural networks are well suited to tasks that involve identifying complex patterns and relationships in large amounts of data.
The simplest form of machine learning is called supervised learning, which involves the use of labeled data sets to train algorithms to classify data or predict outcomes accurately. In supervised learning, humans pair each training example with an output label. The goal is for the model to learn the mapping between inputs and outputs in the training data, so it can predict the labels of new, unseen data.


You must be logged in to post a comment.